Chorda Tympani Nerve Joins Which of the Following Nerves
From the stylomastoid foramen. The chorda tympani is a nerve that branches from the facial nerve cranial nerve VII inside the facial canal just before the facial nerve exits the skull via the stylomastoid foramenIt serves the taste buds in the front of the tongue runs through the middle ear and carries taste messages to the brain.
Chorda Tympani Nerve Earth S Lab
C The zygomaticofacial nerve a branch of the zygomatic nerve that joins the maxillary nerve or second division of the trigeminal nerve or fifth cranial nerve serves as a sensory nerve for the skin of the cheek.

. Injury to the chorda tympani may result in loss or distortion of taste information. The chorda tympani goes between the malleus and incus and re-emerges anterior to the middle ear cavity. The chorda tympani CT nerve carries taste information from the anterior tongue to the brain stem.
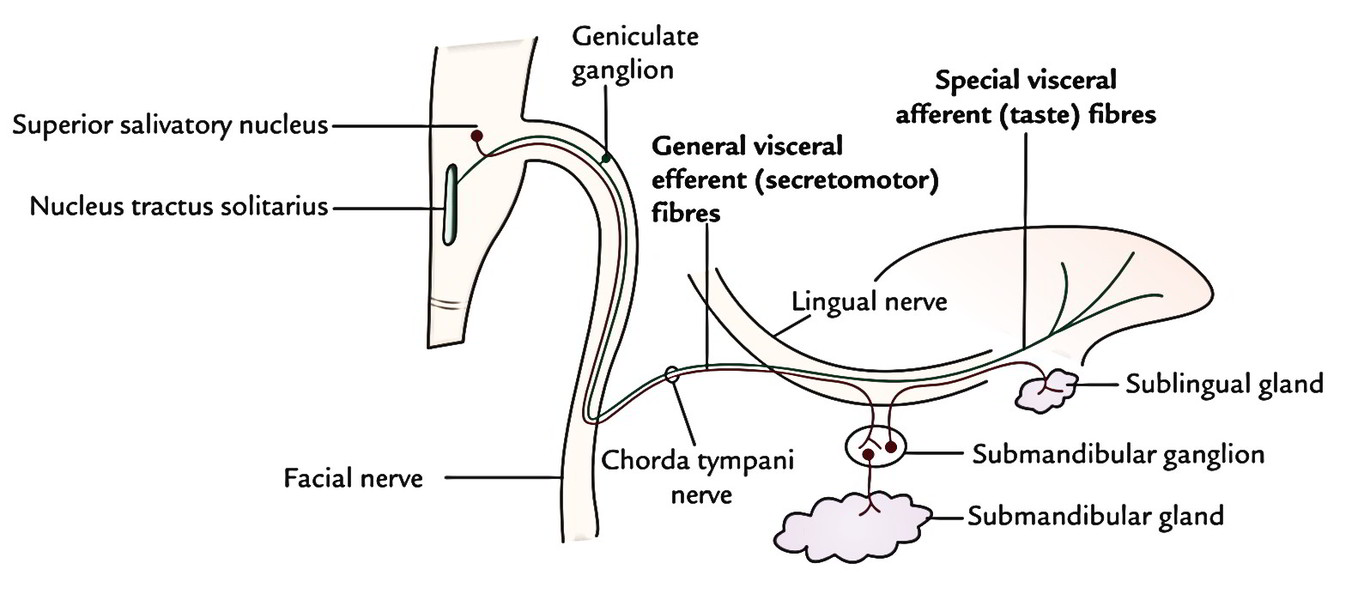
Afferent and efferent central connections of three nerves innervating oral or laryngeal taste buds in the rabbit including the chorda tympani CT the lingual-tonsillar branch of the glossopharyngeal IX and the superior laryngeal nerve SLN were traced by means of horseradish peroxidase neurohistochemistry. Chorda tympani nerve sublingual salivary gland C. Out petrotympanic fissure to join the lingual nerve travels with lingual nerve to synapse at the submandibular ganglion then.
General visceral efferent fibres. In human nervous system. Through internal acoustic meatus and facial canal to chorda tympani through middle ear cavity.
Lingual artery is one of the branches of the external carotid artery and supplies the oral floor and tongue. D The chorda tympani nerve a branch of the facial nerve or seventh cranial nerve is a parasympathetic efferent motor nerve to the. Carries secretomotor fibers to submandibular gland B.
This study examined changes occurring in the hamster peripheral taste system during recovery from. Lingual nerve base of tongue. Vagus nerve temporomandibular joint D.
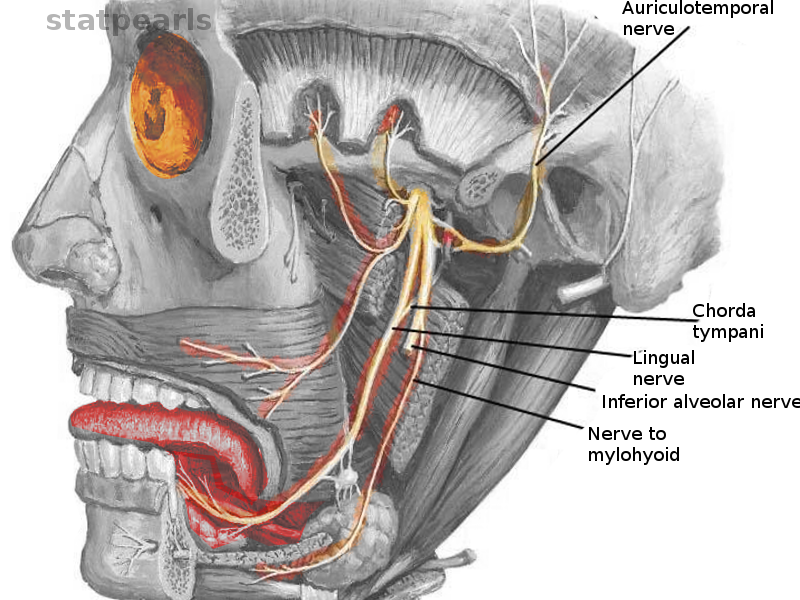
Facial nerve CN VII or 7ganglion by way of the chorda tympani nerve another branch of the facial nerve which joins the lingual branch of the mandibular nerve. Joins lingual nerve in infratemporal fossa C. Facial nerve parotid salivary gland B.
These fibres take taste sensations from anterior ⅔rd of tongue with the exception of vallate papillae. The Chorda Tympani Nerve is given off from the facial as it passes downward behind the tympanic cavity about 6 mm. Contains postganglionic parasympathetic fibers Correct answer.
Chorda tympani is a nerve that arises from the mastoid segment of the facial nerve carrying afferent special sensation from the anterior two-thirds of tongue via the lingual nerve as well. Finally the chorda tympani joins the lingual nerve after exiting the petrotympanic fissure in the infratemporal fossa. Preganglionic parasympathetic fibers of chorda tympani facial nerve course along the lingual nerve to on destination to submandibular ganglion Perception of touch on chin.
Which of the following nerve and innervation pairs is a CORRECT match. Ls a brach of facial nerve D. The chorda tympani is part of one of three cranial nerves that are involved in taste.
TongueLingual artery nerve and chorda tympani. Jaw clench medial and lateral protraction of the jaw against resistance the jaw jerk reflex is used specifically to test for upper motor neuron lesions Buccal. All these are preganglionic parasympathetic secretomotor fibres to submandibular and sublingual salivary glands.
The chorda tympani is a branch of the facial nerve the facial nerve is the nerve of the second arch. It then enters medially to the temporomandibular joint through the petrotympanic fissure. The following statements concerning chorda tympani nerve are true except that it.
The chorda tympani nerve includes. Facial nerve parotid salivary gland B. Lingual nerve base of tongue.
It exits the facial nerve just before it exits via the stylomastoid foramen. The chorda tympani is a nerve that arises from the mastoid segment of the facial nerve carrying afferent special sensation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue via the lingual nerve as well as efferent parasympathetic secretomotor innervation to the submandibular and sublingual glands. Postganglionic fibres from the pterygopalatine ganglion innervate the nasal and palatine glands and the lacrimal gland while those from the submandibular ganglion serve the submandibular.
Chorda tympani nerve sublingual salivary gland C. This is a prospective study that looks into the prevalence of chorda tympani nerve CTN injury and related symptoms following varying degrees of trauma to. Which of the following nerve and innervation pairs is a CORRECTmatch.
The chorda tympani nerve is a branch of facial nerve. It is one of the three cranial nerves that is involved in transmission of taste fibers from the tongue. Vagus nerve temporomandibular joint D.
Special visceral afferent fibres. Contains postganglionic parasympathetic fibers Chorda tympani nerve contains preganglionic. The chorda tympani nerve from the facial nerve via the submandibular ganglion is secretomotor and provides parasympathetic.
It runs upward and forward in a canal and enters the tympanic cavity through an aperture iter chordæ posterius on its posterior wall close to the medial surface of the posterior border of the tympanic membrane and on a. Chorda tympani nerve conveys taste fibers from the anterior 23 of tongue. The chorda tympani carries taste fibres from the front part of tongue a first arch derivative therefore the chorda tympani is the pretrematic branch of the facial nerve.

The Sections Of The Chorda Tympani Between The Facial Nerve And Lingual Download Scientific Diagram

Chorda Tympani Enters Tympanic Cavity Courses Anterior Medial To The Neck Of The Malleus And Leaves Facial Nerve Cranial Nerves Human Anatomy And Physiology
Comments
Post a Comment